Texture System
Ensure you have
v3.3.0+of PixelsWorld
Through this chapter, you can quickly understand and learn how to use the texture system in PixelsWorld.
- newTex
- delTex
- getSize
- swapTex
- drawTo
- castTex
- blendTex
- copyTex
- fetchTex
- savePNG, loadPNG, saveEXR, loadEXR, saveRAW, loadRAW
- rotateTex, flipTex, resizeTex, trimTex
Texture ID
In PixelsWorld, textures are represented by an integer (texture ID). The basic texture IDs provided by PixelsWorld are as follows:
| Texture ID | Lua Mode Global Constant | GLSL Mode Global Constant | Shadertoy Mode Global Constant | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
-3 |
OUTPUT |
Not accessible | Not accessible | Output texture |
-2 |
TEMP |
PW_TEMP_LAYER |
_PixelsWorld_PW_TEMP_LAYER |
Temporary texture |
-1 |
INPUT |
AE_INPUT_LAYER |
_PixelsWorld_AE_INPUT_LAYER |
Input texture |
0 |
PARAM0 |
0 |
0 |
Parameter layer 0 |
1 |
PARAM1 |
1 |
1 |
Parameter layer 1 |
... |
PARAM... |
... |
... |
... |
9 |
PARAM9 |
9 |
9 |
Parameter layer 9 |
You can also create your own texture ID, the method is explained later.
Basic Process
Usually, Ae sends an image to PixelsWorld, which first places the image in INPUT. After computation, the result is placed in the OUTPUT texture. Once all instructions are done, the OUTPUT texture is sent back to Ae as the result.
Role of TEMP
Since OpenGL does not support reading and writing the same texture simultaneously, PixelsWorld provides TEMP to store the results drawn by functions such as glsl, shadertoy, etc. You can use getColor(PW_TEMP_LAYER, uv); to sample the color of TEMP in shaders.
Create Texture
Use newTex(width, height) to create a texture, which returns a texture ID (a random integer value).
Delete Texture
Use delTex(id) to delete a specified texture.
Usually, you don’t need to delete textures manually; PixelsWorld will delete all textures at the end of each frame. However, it's a good habit to free up video memory when a texture is no longer needed.
Get Size
Use getSize(id) to get the dimensions of a texture.
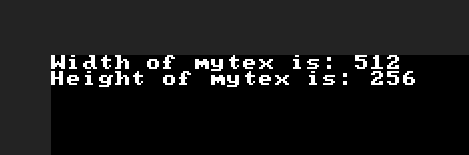
getSize.lua
version3()
mytex = newTex(512,256)
w,h = getSize(mytex)
println("Width of mytex is: " .. w)
println("Height of mytex is: " .. h)
Swap Textures
Use swapTex(id1, id2) to swap the textures represented by id1 and id2.
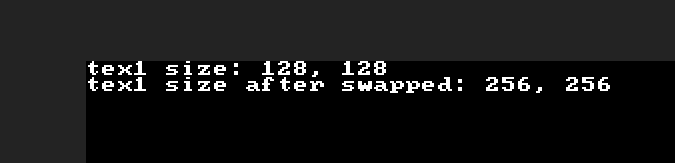
swapTex.lua
version3()
tex1 = newTex(128,128)
tex2 = newTex(256,256)
w, h = getSize(tex1)
println("tex1 size: " .. w .. ", " .. h)
swapTex(tex1, tex2)
w, h = getSize(tex1)
println("tex1 size after swapped: " .. w .. ", " .. h)
Set Draw Texture
Use drawTo(id) to change the draw texture. The default draw texture is OUTPUT. Note: PixelsWorld will ultimately use OUTPUT as the result to send to Ae. The following three methods can send results to OUTPUT from other textures:
Cast Texture
Use castTex(toTexId, fromTexId) to project pixels from fromTexId to toTexId. For example, you can project parameter layer 0 PARAM0 to the output texture OUTPUT:
castTex.lua
version3()
castTex(OUTPUT, PARAM0)
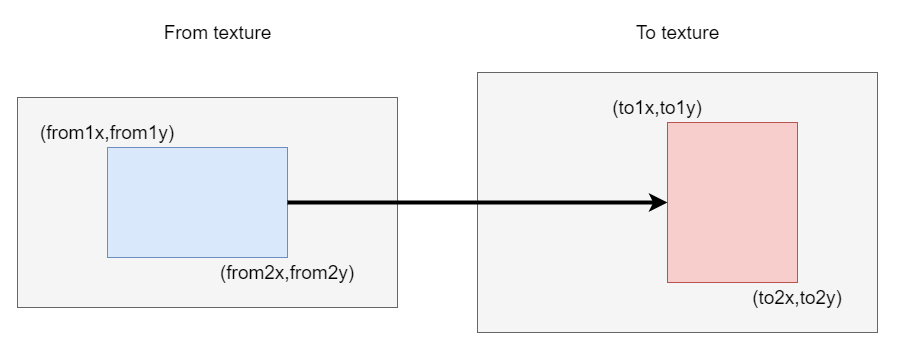
You can also specify the range of the cast texture (with the texture's top-left corner as the origin):
castTex(toTexId, fromTexId, to1x, to1y, to2x, to2y)castTex(toTexId, fromTexId, to1x, to1y, to2x, to2y, from1x, from1y, from2x, from2y)
Default is to use the entire texture when the range is omitted.
Blend Textures
Use blendTex(toTexId, fromTexId, blendRule) to use blending rule blendRule to paste texture fromTex onto texture toTex.
blendRulecan be any ofNORMAL, ADD, SUBTRACT, MULTIPLY, DIVIDE, MAX, MIN.blendRulecan also be a string, with rules as follows:Arepresents pixels fromtoTexIdBrepresents pixels fromfromTexIdCrepresents output pixels totoTexId
For example, you can use the following code to blend the image from the input texture with parameter layer 0 using addition:
blendRule.lua
version3()
castTex(OUTPUT, INPUT) -- Cast INPUT texture to OUTPUT firstly.
blendTex(OUTPUT, PARAM0, "C=A+B") -- Blend PARAM0 to OUTPUT.
Internally, this string is translated into GLSL code. The "C=A+B" translates into the following GLSL code:
blendRuleGLSL.frag
#version 330 core
out vec4 outColor;
in vec2 uv;
in vec2 uv2;
uniform sampler2D inLayerA;
uniform sampler2D inLayerB;
void main(){
vec4 A = texture(inLayerA, uv);
vec4 B = texture(inLayerB, uv2);
vec4 C = A;
C=A+B // Your blend rule is combined here.
;
outColor = C;
}
Like castTex, blendTex also supports specifying the texture range for blending:
blendTex(toTexId, fromTexId, blendRule, to1x, to1y, to2x, to2y)blendTex(toTexId, fromTexId, blendRule, to1x, to1y, to2x, to2y, from1x, from1y, from2x, from2y)

Copy Texture
Use copyTex(refTexId) to copy a texture and return the newly copied texture.
Fetch Any Time Layer Pixel
Use fetchTex(layerId, time) to get the image at a specific time from a specified layer, returning the captured texture ID.
- layerId: Only
PARAM0~PARAM9can be input. - time: Layer time (floating point number, in seconds)
- Note: Using this function may cause Ae’s cache errors; please clear the cache regularly.
- Function added in
v3.4.3+.
Read and Save Textures
Use savePNG(utf8Path, texId), loadPNG(utf8Path) to save and read PNG images.
Use saveEXR(utf8Path, texId), loadEXR(utf8Path) to save and read EXR images.
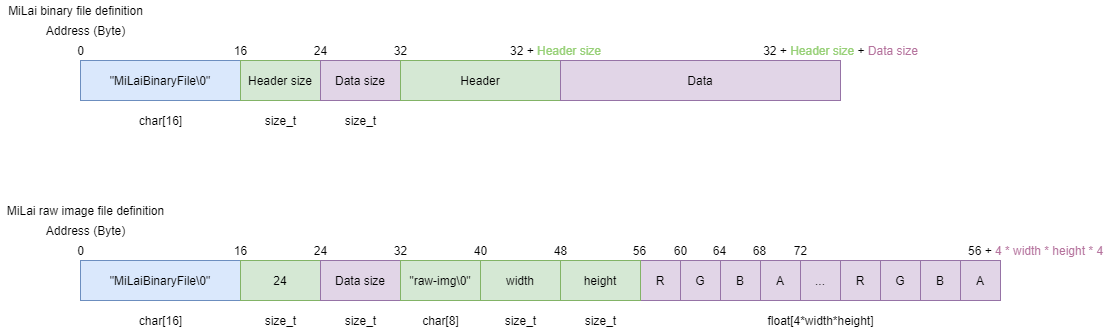
Use saveRAW(utf8Path, texId), loadRAW(utf8Path) to save and read MiLai’s original uncompressed memory images.
Here are the image specifications supported by PixelsWorld:
| Format | Library Used | Supported Compression Method | Image Color Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| PNG | cute_headers | DEFLATE compliant decompressor zlib(RFC 1950) | RGBA, clamped 8bit unsigned integer per channel. |
| EXR | tinyexr | NONE, RLE, ZIP, ZIPS, PIZ, ZFP | RGBA, HDR 32bit floating point per channel. |
| RAW | (None) | MiLai original format. (See figure below) | RGBA, HDR 32bit floating point per channel. |
Read a PNG image into the scene:
loadPNG.lua
version3()
local mypng = loadPNG([[d:\test.png]]) -- Replace with your path.
castTex(OUTPUT, mypng) -- Cast pixels from mypng to OUTPUT.
Save a PNG image to local storage:
savePNG.lua
version3()
--Draw something to OUTPUT
move(width/2, height/2)
rotate(time)
triangle()
--End drawing.
savePNG([[d:\test.png]], OUTPUT) -- Save OUTPUT as PNG to local disk. Replace with your path here.
- Replace
PNGwithEXRto save and read EXR images.- Saving to certain locations may require administrator permissions.
Adjust Texture
Use rotateTex(texId, times) to rotate the texture by 90*times degrees, where rotateTex(texId) is equivalent to rotateTex(texId, 1).
Use flipTex(texId, flipV) to flip the texture, where flipV is a boolean value. flipV is true for vertical mirroring and false for horizontal mirroring.
Use resizeTex(texId, width, height) to scale the texture.
Use trimTex(texId, p1x, p1y, p2x, p2y) to crop the texture. p1x, p1y, p2x, p2y are coordinates with the texture's top-left corner as the origin.