Function List
Below is a list of functions defined in Lua mode for PixelsWorld.
Mandatory Declaration Function
Parameter Retrieval Functions
slider, angle, point, point3d, checkbox, color, layer
Output Information Functions
Transformation Functions
move, scale, rotate, rotateX, rotateY, rotateZ, twirl
beginGroup, endGroup, beginGlobal, endGlobal
global2local, local2global, global2screen, screen2global
Drawing Functions
Primitives
tri, quad, rect, circle, ellipse, par, line
image, imageAlign, imageAnchor
text, textSize, textFont, textAlign, textAnchor, textAlignOuter, textInterval, textAdvanceScale
Drawing Attribute Controls
fill, noFill, stroke, noStroke, dot, noDot
Lighting
newLight, delLight, getLightInfo
activateLight, deactivateLight, getActivatedLight, setActivatedLight
ambientLight (legacy), pointLight (legacy), parallelLight (legacy)
clearLight (legacy), getLight (legacy)
Camera
Stroked Detail
strokeWidth, strokeDivision, strokeGlobal, strokeLocal
Dot Rendering Detail
dotRadius, dotDivision, dotGlobal, dotLocal
Output Detail
Texture Manipulation
Utilities
map clamp step smoothStep bezier
rgb2hsl,hsl2rgb,rgb2hsv,hsv2rgb,rgb2cmy,cmy2rgb,rgb2cmyk,cmyk2rgb,cmy2cmyk,cmyk2cmy,hsl2hsv,hsv2hsl
getGLInfo, getDrawRecord, getStatus
Pixel Reading and Writing Functions
Code Execution Functions
shadertoy, glsl, cmd, lua, runFile, txt
Detailed Explanation
version3
The function version3() must be declared in the first line in Lua mode. Its purpose is to import all functions under the pw3 table into the global scope. If this line is missing, you need to prefix all functions provided by PixelsWorld with pw3., such as the println() function, which would need to be written as pw3.println(). Conversely, if you call the version3() function at the beginning of your code, you do not need the pw3. prefix. This design is intended to ensure backward compatibility with your code. We recommend that you include a call to version3() in the first line of any Lua rendering mode code in all circumstances.
version3.lua
version3()
println("Hello PixelsWorld! ")
without_version3.lua
pw3.println("Hello PixelsWorld! ")
print(str), print(str,brightness), print(str,r,g,b), print(str,r,g,b,a) are functions to output information on the top left corner of the screen.
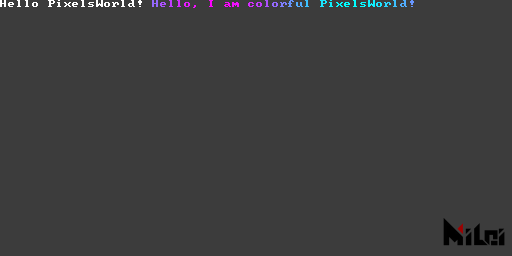
print.lua
version3()
print("Hello PixelsWorld! ")
str = "Hello, I am colorful PixelsWorld! "
for i=1,#str do
local c = str:sub(i,i)
local phase = math.sin(i/#str*TPI + time*10) / 2 + .5
print(c,phase,1-phase,1,1)
end
println
println(str), println(str, brightness), println(str, r, g, b), println(str, r, g, b, a) are functions for outputting information in the top left corner of the screen, with each output followed by a newline.
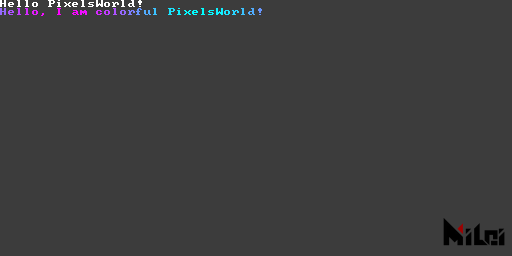
println.lua
version3()
println("Hello PixelsWorld! ")
str = "Hello, I am colorful PixelsWorld! "
for i=1,#str do
local c = str:sub(i,i)
local phase = math.sin(i/#str*TPI + time*10) / 2 + .5
-- println(c,phase,1-phase,1,1)
print(c,phase,1-phase,1,1)
end
alert
alert(str) is a function to output warning messages in the top left corner of the screen. It is currently equivalent to println(str, 1, 1, 0, 1).

alert.lua
version3()
alert("Warning: Write your message here! ")
move
move(x,y),move(x,y,z)moves Paintbrush.
All transformations are performed based on the current Paintbrush coordinates.
Example:

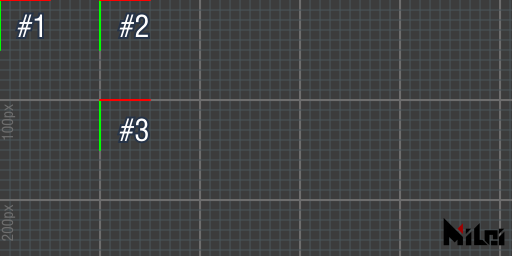
move.md
version3()
coord() -- Display Paintbrush position before transformation
move(100,0)
coord() -- Display Paintbrush position after 1st transformation
move(0,100)
coord() -- Display Paintbrush position after 2nd transformation
Eventually, the Paintbrush will be at position (100, 100, 0).
scale
scale(ratio),scale(x,y),scale(x,y,z)scales the Paintbrush coordinate.
All transforms are done basing on the Paintbrush coordinate.

scale.lua
version3()
move(100,100)
scale(2)
rect(50,25)

no_scale.lua
version3()
move(100,100)
--scale(2)
rect(50,25)
rotate
rotateX
rotateY
rotateZ
rotate(theta) is a function to rotate the Paintbrush coordinates by theta radians, rotateX(theta) rotates the Paintbrush coordinates along its X-axis, and rotate(theta) is essentially equivalent to rotateZ(theta).
- All transformations are performed based on the current Paintbrush coordinates.
- If you are unfamiliar with radians, you can use the function
d2r(degree)to convert degrees into radians. For example:rotate(d2r(90))rotates by ninety degrees.

rotate_degree.lua
version3()
move(100, 100)
rotate(d2r(45))
rect(50, 25)

rotate_radian.lua
version3()
move(100, 100)
rotate(PI/4)
rect(50, 25)

rotateX.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(100, 100)
grid()
coord()
rotateX(d2r(45))
cube(50, 25, 10)

rotateY.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(100, 100)
grid()
coord()
rotateY(d2r(45))
cube(50, 25, 10)

rotateZ.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(100, 100)
grid()
coord()
rotateZ(d2r(45))
cube(50, 25, 10)
twirl
twirl(theta, x, y, z) is a function to rotate the Paintbrush coordinate along the (x, y, z) axis by theta radians. For instance, the above rotateX(theta) is equivalent to twirl(theta, 1, 0, 0).
- All transformations are performed based on the current PaintBrush coordinates.
twirluses a matrix implementation for quaternion rotation.

twirl.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(100, 100)
grid()
coord()
stroke(1, 1, 0)
line(-50, -50, -50, 50, 50, 50)
stroke(0, 0, 0)
twirl(d2r(90), 1, 1, 1)
cube(50, 25, 10)
beginGroup
endGroup
beginGroup(),endGroup()are functions to create parent-child relationships. Transformations (move, scale, rotate, twirl) betweenbeginGroup()andendGroup()are undone afterendGroup().beginGroup(mat)creates a parent-child relationship and pushes a 4x4 matrix mat into the scene (you can use getTransformMatrix to obtain transformation matrix).
It is equivalent to
pushMatrix()andpopMatrix()in Processing.
For example, the following two code blocks are equivalent:

group.lua
version3()
for i = 1, 6 do
beginGroup()
move(i * 25, i * 25)
rotate(d2r(15 * i))
rect(25)
endGroup()
end

without_group.lua
version3()
for i = 1, 6 do
move(i * 25, i * 25)
rotate(d2r(15 * i))
rect(25)
rotate(d2r(-15 * i))
move(-i * 25, -i * 25)
end
beginGlobal
endGlobal
Drawing functions enclosed in beginGlobal, endGlobal
will temporarily draw in the global coordinate system.
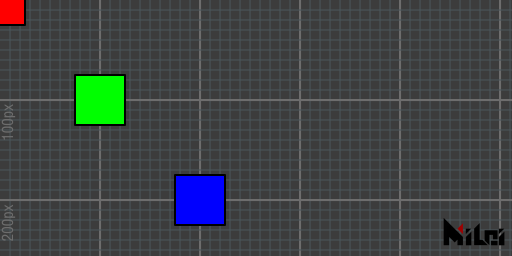
beginGlobal.lua
version3()
move(100, 100)
fill(0, 1, 0) -- green
rect(50) -- Draw on (100, 100, 0)
beginGlobal()
fill(1, 0, 0) -- red
rect(50) -- Draw on (0, 0, 0)
endGlobal()
move(100, 100)
fill(0, 0, 1) -- blue
rect(50) -- Draw on (200, 200, 0)
global2local
global2local(x, y, z) converts global coordinates to local coordinates and returns three double values.
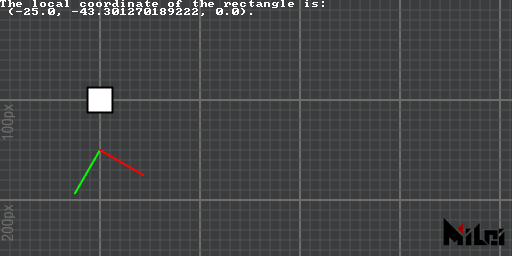
global2local.lua
version3()
move(100, 100)
rect(25)
move(0, 50)
rotate(d2r(30))
coord()
x, y, z = global2local(100, 100, 0)
println("The local coordinate of the rectangle is:\n (" .. x .. ", " .. y .. ", " .. z .. ").")
local2global
local2global(x, y, z) converts local coordinates to global coordinates and returns three doubles.
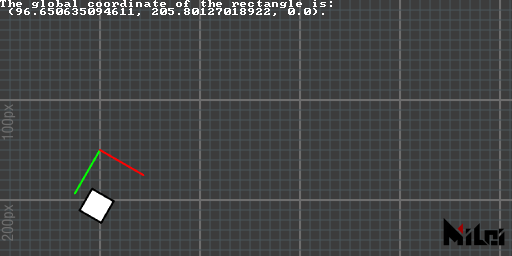
local2global.lua
version3()
move(100, 100)
move(0, 50)
rotate(d2r(30))
coord()
move(25, 50)
rect(25)
x, y, z = local2global(0, 0, 0)
println("The global coordinate of the rectangle is:\n (" .. x .. ", " .. y .. ", " .. z .. ").")
global2screen
global2screen(x, y, z) converts global coordinates to screen coordinates and returns three doubles.
This conversion is affected by perspective mode.
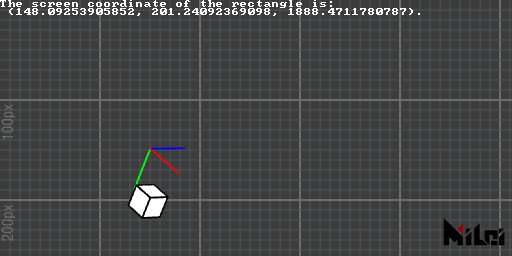
global2screen.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(100, 100, 0)
move(0, 50, 0)
rotateZ(d2r(30))
coord()
move(25, 50, 0)
cube(25)
x, y, z = global2screen(local2global(0, 0, 0))
println("The screen coordinate of the rectangle is:\n (" .. x .. ", " .. y .. ", " .. z .. ").")
screen2global
screen2global(x, y, z) converts screen coordinates to global coordinates and returns three doubles.
This conversion is affected by perspective mode.
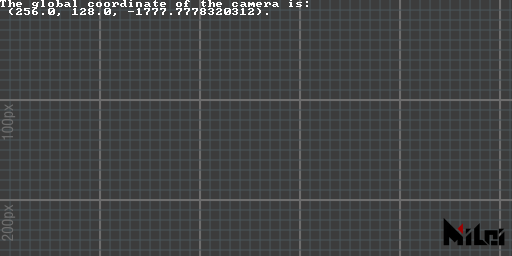
screen2global.lua
version3()
dim3()
x, y, z = screen2global(0, 0, 0)
println("The global coordinate of the camera is:\n (" .. x .. ", " .. y .. ", " .. z .. ").")
getTransformMatrix
getTransformMatrix() returns a column-major 4x4 transformation matrix. This transformation matrix can be applied in beginGroup(mat).
mat[i][j]can access the element at columni, rowj. (i,jrange 1~4)
Example:
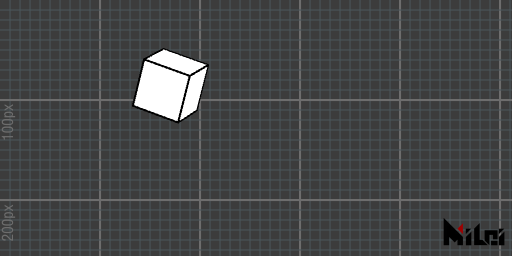
matrix.lua
version3()
dim3()
beginGroup()
move(width/3, height/3)
twirl(d2r(30), 1, 1, 1)
cubetransform = getTransformMatrix()
endGroup()
beginGroup(cubetransform)
cube(50)
endGroup()
tri
tri(radius)creates an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle with radiusradiusand points in the positive y-direction of the Paintbrush coordinate.tri()is equivalent totri(100)tri(w, h)creates an isosceles triangle with basewand heighth.tri(p1x, p1y, p2x, p2y, p3x, p3y)creates a triangle with vertices at the 2D pointsp1, p2, p3.tri(p1x, p1y, p1z, p2x, p2y, p2z, p3x, p3y, p3z)creates a triangle with vertices at the 3D pointsp1, p2, p3.
- To observe a 3D triangle, please add
dim3()after theversion3()function and set up a camera view in the Ae layer.- Triangles constructed by the first three methods have normals by default in the negative direction of the z-axis of the Paintbrush coordinate, while the triangles from the last two are geometrically normal by
cross(p1-p2, p3-p2).- The function name is a shorthand for
triangle.
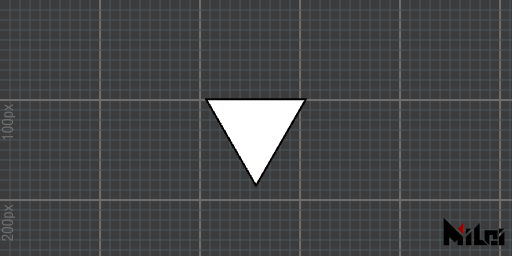
tri1.lua
version3()
move(width/2, height/2)
tri(100)
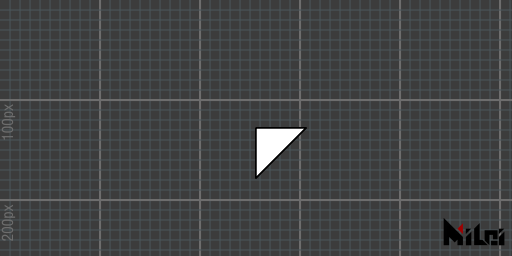
tri5.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(width/2, height/2)
tri(0, 0, 100, 50, 0, 0, 0, 50, 0)
quad
quad(p1x, p1y, p2x, p2y, p3x, p3y, p4x, p4y)quad(p1x, p1y, p1z, p2x, p2y, p2z, p3x, p3y, p3z, p4x, p4y, p4z)
- Draw the first triangle in the order of
p1, p2, p3, and the second triangle in the order ofp1, p3, p4.
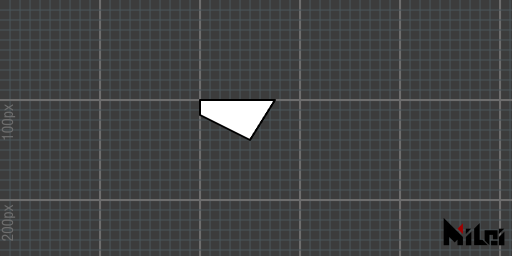
quad.lua
version3()
move(200, 100)
quad(0, 0, 75, 0, 50, 40, 0, 15)
rect
rect(size)draws a square with the given size.rect()is equivalent torect(100)rect(width, height)draws a rectangle with the specifiedwidthandheight.
- The rectangle is generated with its center as the intersection point of the diagonal in the Paintbrush coordinate system.
- The function name is a shorthand for
rectangle.
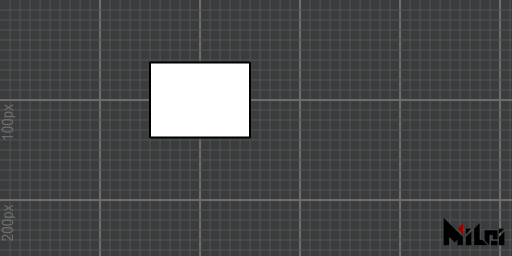
rect.lua
version3()
move(200, 100)
rect(100, 75)
circle
circle(radius)draws a circle with a radius ofradius.circle()is equivalent tocircle(100)circle(radius, div)draws a circle with a radius ofradiusanddivsegments.
The default number of segments is 128.
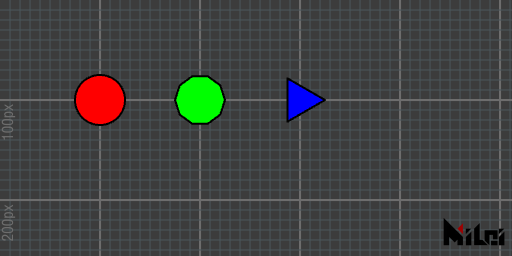
circle.lua
version3()
move(100, 100)
fill(1, 0, 0)
circle(25)
move(100, 0)
fill(0, 1, 0)
circle(25, 10)
move(100, 0)
fill(0, 0, 1)
circle(25, 3)
ellipse
ellipse(radiusx, radiusy)draws an ellipse with an x-radius ofradiusxand a y-radius ofradiusy.ellipse()is equivalent toellipse(100, 100)ellipse(radiusx, radiusy, div)draws an ellipse with an x-radius ofradiusx, a y-radius ofradiusy, anddivsegments.
The default number of segments is 128.
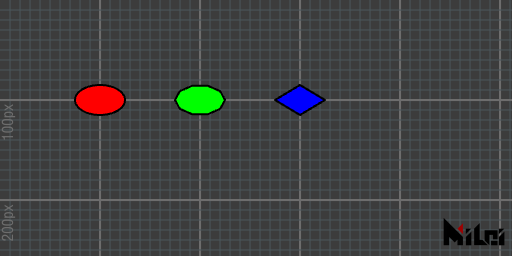
ellipse.lua
version3()
move(100, 100)
fill(1, 0, 0)
ellipse(25, 15)
move(100, 0)
fill(0, 1, 0)
ellipse(25, 15, 10)
move(100, 0)
fill(0, 0, 1)
ellipse(25, 15, 4)
line
line(p1x, p1y, p2x, p2y)draws a line segment.line(p1x, p1y, p1z, p2x, p2y, p2z)draws a 3D line segment.line()is equivalent toline(0, 0, 0, 100, 100, 100)
- The color of the line is controlled by
stroke(r, g, b).- The thickness of the line is controlled by
strokeWidth(width).- Lines are rendered by default; to disable line rendering, use
noStroke(), and to enable it, usestroke().

line.lua
version3()
move(200, 100, 0)
stroke(1, 0, 0)
line(0, 0, 0, 50)
move(100, 0, 0)
stroke(0, 1, 0)
line(0, 0, 0, 50)
move(100, 0, 0)
stroke(0, 0, 1)
line(0, 0, 0, 50)
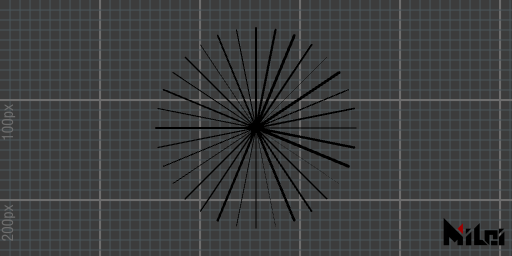
line_circle.lua
version3()
math.randomseed(1)
num = 32
move(width/2, height/2)
for i=1, num do
beginGroup()
rotateZ(d2r(360/num*i))
strokeWidth(math.random()*3)
line(0, 0, 100, 0)
endGroup()
end
par
par(x)draws a point at position(x,0,0).par(x, y)draws a point at position(x, y, 0).par(x, y, z)draws a point at position(x, y, z).par()is equivalent topar(0,0,0).
- Point rendering is off by default; use
dot()to enable it. You can disable it at any time withnoDot().- The radius of the point is controlled by
dotRadius(radius).- The color of the point is controlled by
dot(r, g, b).- If you do not want the point to be distorted or shrunk, use
dotGlobal(). By default, points are rendered indotLocal()mode.
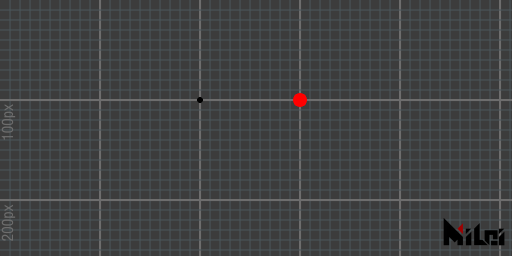
par.lua
version3()
dot()
dotRadius(3)
move(200, 100)
par()
dot(1, 0, 0)
dotRadius(7)
move(100, 0)
par()
cube
cube(size)draws a cube with a side length ofsize.cube(sizex, sizey, sizez)draws a cuboid with dimensionssizex, sizey, sizez.cube()is equivalent tocube(100).
The normals of the cuboid are outward by default. Negative lengths or the use of
scale()with a negative sign may result in inward normals.
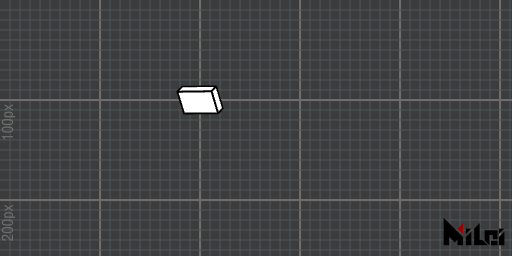
cube.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(200, 100, 0)
rotateY(d2r(30))
rotateX(d2r(30))
cube(40, 25, 10)
tet
tet(radius)draws an inscribed regular tetrahedron with a spherical radius ofradius.tet()is equivalent totet(50).tet(p1x, p1y, p1z, p2x, p2y, p2z, p3x, p3y, p3z, p4x, p4y, p4z)draws a tetrahedron with vertices atp1, p2, p3, p4.
- The normals of tetrahedra drawn using the third method are determined by the drawing order: vertices are drawn in the order
p1, p2, p3; p2, p1, p4; p3, p2, p4; p1, p3, p4. Please refer to thetrisection for triangle normal directions.- The function name is a shorthand for
tetrahedron.
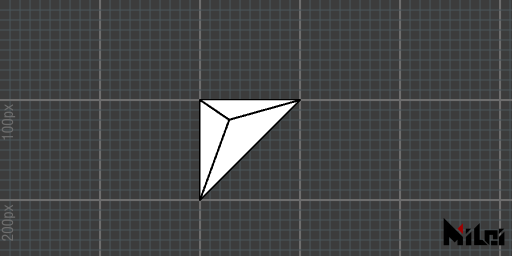
tet.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(200, 100, 0)
tet(0, 0, 0,
100, 0, 0,
0, 100, 0,
30, 20, -50
)
cone
cone(size)draws a cone with a base radius ofsizeand height2*size.cone()is equivalent tocone(50).cone(radius, height)draws a cone with a radius ofradiusand height ofheight.cone(radius, height, div)draws a cone with a radius ofradius, height ofheight, and segmented intodivsections.
- The default number of segments is 64.
- When the number of segments is greater than 16, the cone face outlines and base vertices will be hidden.
- Negative input values or the use of
scale()with a negative sign may result in inward normals.
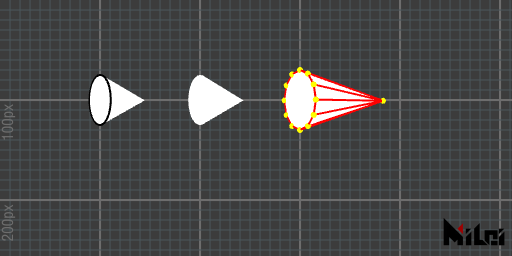
cone.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(100, 100, 0)
beginGroup()
rotateY(d2r(60))
cone(25)
endGroup()
move(100, 0, 0)
beginGroup()
rotateY(d2r(60))
noStroke()
cone(25)
endGroup()
move(100, 0, 0)
beginGroup()
rotateY(d2r(60))
stroke(1, 0, 0)
dot(1, 1, 0)
dotRadius(3)
cone(30, 100, 12)
endGroup()
ball
ball(radius)draws a 3D sphere with a radius ofradius.ball()is equivalent toball(50).ball(radius, level)draws a sphere with a radius ofradiusand subdivision level oflevel.
- The default level is 4.
- Level must be greater than or equal to 0.
- A level of 0 results in an octahedron.
- When the level is greater than 2, outlines and vertices will be hidden.
- Negative input values or the use of
scale()with a negative sign may result in inward normals.
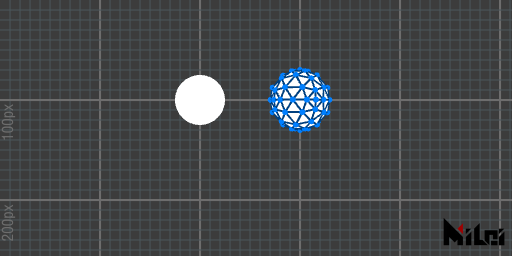
ball.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(200, 100, 0)
beginGroup()
rotateY(d2r(60))
ball(25)
endGroup()
move(100, 0, 0)
beginGroup()
rotateY(d2r(60))
stroke(0, 0.25, 0.5)
dot(0, 0.5, 1)
dotRadius(3)
ball(30, 2)
endGroup()
tube
tube(size)draws a cylinder with a base radius ofsizeand height2*size.tube()is equivalent totube(50).tube(radius, height)draws a cylinder with a radius ofradiusand height ofheight.tube(radius1, radius2, height)draws a cylinder with a base radius ofradius1near the Paintbrush coordinate origin, a base radius ofradius2on the far side, and height ofheight.tube(radius1, radius2, height, div)adds segment control to the fourth function.tube(radius1, radius2, height, div, needMesh)adds a boolean to control whether to render the two circular faces based on the fifth function.tube(radius1, radius2, height, div, needMesh1, needMesh2)adds booleansneedMesh1to control rendering of the near side base andneedMesh2for the far side base based on the fifth function.
divdefaults to 64.needMeshdefaults totrue.- When the number of segments is more than 16, the cylinder's side outlines and vertices on both bases will be hidden.
- Negative input values or the use of
scale()with a negative sign may result in inward normals.
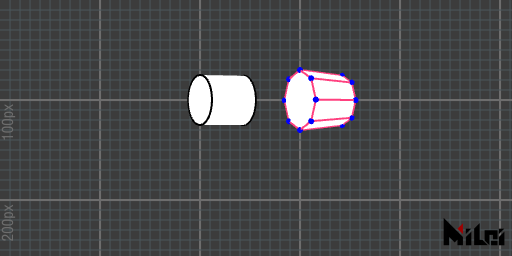
tube.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(200, 100, 0)
beginGroup()
rotateY(d2r(60))
tube(25)
endGroup()
move(100, 0, 0)
beginGroup()
rotateY(d2r(60))
stroke(1, 0.25, 0.5)
dot(0, 0, 1)
dotRadius(3)
tube(30, 25, 50, 8)
endGroup()
image
image(id, width, height)draws an image of specifiedwidthandheightonto the scene.
idis the texture identifier,PARAM0toPARAM9are textures obtained from the plugin panel's layer controls,INPUTis the input image to the plugin, andOUTPUTis the output image.- Specifying
OUTPUTasidtriggers a screen capture action of the current drawing sinceOUTPUTis the texture used as your drawing board, making it slightly slower than other parameters.- The difference between this function and
in2out(id)is thatimage(id, width, height)interacts with the scene's depth information based on the Paintbrush coordinates. This means the image is rendered upside down by default, as Ae's coordinate system has a downward y-axis; you should add arotateX(PI)before to correct this (usingscale(1, -1)is not recommended, as it could cause incorrect normals in subsequent shapes). In contrast,in2out(id)ignores depth information and writes pixels directly onto the current drawing board (without the upside-down issue).
The example below demonstrates a cube interacting with the input image.
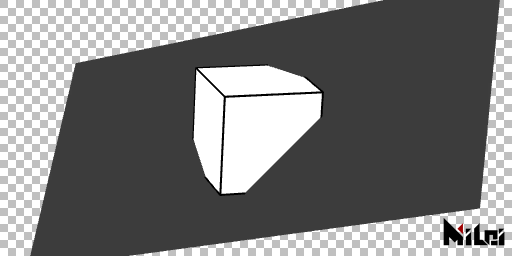
render_image.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(width/2, height/2)
twirl(d2r(45), -1, 1, 0)
beginGroup()
rotateX(d2r(180))
image(INPUT, width, height)
endGroup()
twirl(d2r(60), 1, 1, 1)
cube()
imageAlign
New in
v3.3.0.
Use imageAlign(rule) to change the orientation of the image in the image function. rule follows these rules:
ruleis a string of length 4.- The 1st character is
+or-. - The 2nd character is one of
x, y, z. - The 3rd character is
+or-. - The 4th character is one of
x, y, z.
rule specifies how the UV coordinates of an image (origin at the lower left corner) align with the axes of the Paintbrush coordinate system. The default rule is "+x+y", meaning the u-axis aligns with positive x and the v-axis with positive y.

imageAlign.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(100, 100, 0)
coord()
image(PARAM0, 128, 128)
move(150, 0, 0)
coord()
imageAlign("+x-y")
image(PARAM0, 128, 128)
move(150, 0, 0)
coord()
imageAlign("+z-y")
image(PARAM0, 128, 128)
imageAnchor
New in
v3.5.0.
imageAnchor(u, v)specifies the position of the image anchor point.imageAnchor(a)is a shorthand forimageAnchor(a, a).

text
New in
v3.5.0
text(str) is used to render text on the screen.

text.lua
version3()
move(width/2, height/2)
textAlign("+x-y")
text("Hello PixelsWorld!")
You can also use the following functions to change the text style:
- Text fill color: fill(r,g,b)
- Text stroke color: stroke(r,g,b)
- Disable fill: noFill()
- Disable stroke: noStroke()
- Stroke thickness: strokeWidth(width)
- Font: textFont(fontFileName)
- Font size: textSize(size)
- Letter spacing: textInterval(dx,dy)
- Text width proportional scaling: textAdvanceScale(rx,ry)
textSize
New in
v3.5.0
textSize(size, resolution)sets the size and resolution for the text to be drawn.sizecontrols the text size, andresolutioncontrols the text resolution.textSize(size)is equivalent totextSize(size, size)

textSize.lua
version3()
textAlign("+x-y")
textAnchor(0, 1)
for i = 1, 13 do
local sz = i + 8
textSize(sz)
text("~MiLai visual performance group~")
move(0, sz + 4)
end
textFont
New in
v3.5.0
textFont(fontFileName)sets the font for the text to be drawn.fontFileNameis the file name of the font within theC:\Windows\Fontsfolder (you can see the file name by checking the properties through right-click).
You can also enter the full path of the font file. This means you can access fonts from any location (e.g.,
textFont([[D:\MyFolder\arial.ttf]])).

textFont.lua
version3()
textAlign("+x-y")
textAnchor(0, 1)
textSize(20)
font_list = {
{"arial.ttf", "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."},
{"MATURASC.TTF", "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."},
{"KUNSTLER.TTF", "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."},
{"msmincho.ttc", "色は匂へど 散りぬるを"},
{"UDDigiKyokashoN-R.ttc", "我が世誰ぞ 常ならむ"},
{"STXINGKA.TTF", "人生得意须尽欢 莫使金樽空对月"},
{"msjh.ttc", "山氣日夕佳 飛鳥相與還"},
{"simsun.ttc", "吥葽 莣記莪、伱知道 莪 拿起伱 就 倣吥丅。"},
{"STZHONGS.TTF", "○●対沵倾注ㄋ珴所侑旳温柔︶ㄣ"},
}
for i = 1, #font_list do
textFont(font_list[i][1])
text(font_list[i][2])
move(0, 28)
end
textAlign
New in
v3.5.0
textAlign(rule) is used to set the rendering orientation of the font. rule is the same as in imageAlign(rule).
textAnchor
New in
v3.5.0
textAnchor(x, y) is used to set the anchor point position of the font.
textAlignOuter
New in
v3.5.0
textAlignOuter(flag) sets whether to align the text using the outer outline. flag is a boolean value.
textInterval
New in
v3.5.0
textInterval(x, y) sets the spacing for text mapping. Default is x:0, y:0.
textAdvanceScale
New in
v3.5.0
textAdvanceScale(rx, ry) controls the advancement scaling of text mapping. Default is rx:1, ry:1.
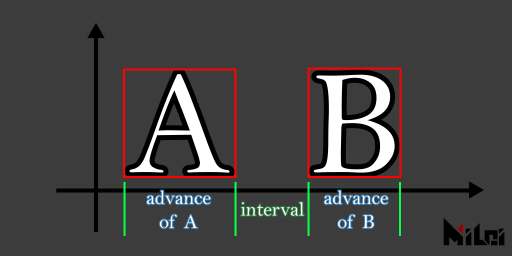
coord
coord() visualizes the current Paintbrush coordinates.
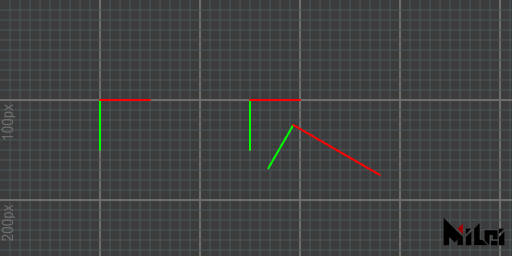
coord.lua
version3()
move(100, 100)
coord()
move(150, 0)
coord()
rotate(d2r(30))
move(50, 0)
scale(2, 1)
coord()
grid
grid() visualizes a grid on the xy plane at the current Paintbrush coordinates with a grid size of 100x100.

grid.lua
version3()
move(width/2, height/2)
rotate(d2r(30))
grid()
setPoly
setPoly(obj) can pre-parse the object information to be drawn. After setting, you can call poly() to quickly render the object that was just set.
- When you draw the same object multiple times in a scene, using this function to set the object in advance will be efficient.
- For information on constructing
obj, please refer to the Poly section.
background
background(brightness), background(r,g,b), background(r,g,b,a) fills the current canvas with the specified color.
- Note: If you have previously drawn shapes, they will be covered.

background.lua
version3()
background(1, 1, 0)
in2out
in2out(id)sets the specified layer parameter as the background.in2out()is equivalent toin2out(INPUT), which uses the input layer as the background.
idrange:PARAM0~PARAM9orINPUT.
dim2
dim2() uses 2D drawing mode. This is enabled by default, so you generally do not need to call it.
Essentially, 2D mode in PixelsWorld is an orthographic 3D mode without depth information.
dim3
dim3() switches to 3D drawing mode. We recommend declaring it right after version3().
Note: When rendering 3D shapes on a layer different from the composition size, use
viewSpaceto change the camera's far plane size to avoid unexpected positioning results.
perspective
perspective() renders using a perspective view, where objects follow the rule of being larger when closer and smaller when farther. You can use viewSpace to adjust camera information and lookAt to adjust the camera position.
If you have called
dim3(), the perspective mode is enabled by default.
noPerspective
noPerspective() renders using an orthographic view, where parallel edges of objects remain parallel in the rendered view.
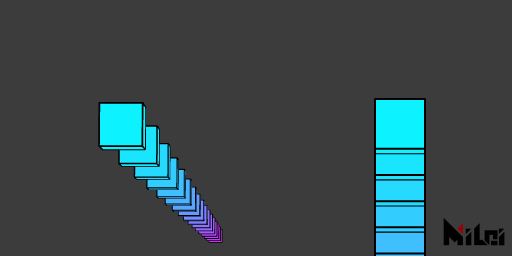
noPerspective.lua
version3()
dim3()
n = 20
move(100, 100, 0)
beginGroup()
rotateX(d2r(85))
for i = 1, n do
move(0, 300, 0)
fill(i/n, 1-i/n, 1)
cube(50)
end
endGroup()
move(300, 0, 0)
noPerspective()
beginGroup()
rotateX(d2r(85))
for i = 1, n do
move(0, 300, 0)
fill(i/n, 1-i/n, 1)
cube(50)
end
endGroup()
fill
fill()enables fill, which is enabled by default.fill(brightness),fill(r, g, b),fill(r, g, b, a)enables fill and sets the fill color.
- Note: In 3D mode, if you set the fill transparency to a value less than 1, render objects from farthest to nearest. Otherwise, objects in front may completely obscure those behind them. (This is a characteristic of OpenGL rendering.)
noFill
noFill() disables the fill.
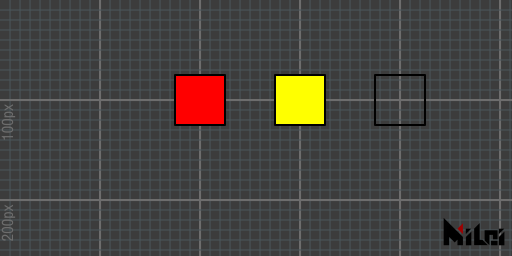
fill.lua
version3()
move(200, 100, 0)
fill(1, 0, 0)
rect(50)
move(100, 0, 0)
fill(1, 1, 0)
rect(50)
move(100, 0, 0)
noFill()
rect(50)
stroke
stroke()enables stroke. It is enabled by default.stroke(brightness),stroke(r, g, b),stroke(r, g, b, a)enables stroke and sets the stroke color.
noStroke
noStroke() disables the stroke.
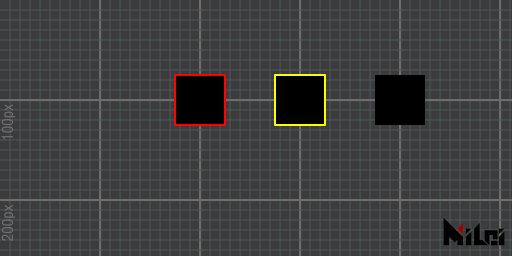
stroke.lua
version3()
fill(0)
move(200, 100, 0)
stroke(1, 0, 0)
rect(50)
move(100, 0, 0)
stroke(1, 1, 0)
rect(50)
move(100, 0, 0)
noStroke()
rect(50)
dot
dot()enables vertex rendering, which is disabled by default.dot(brightness),dot(r, g, b),dot(r, g, b, a)enables vertex rendering and sets the vertex rendering color.
noDot
noDot() disables vertex rendering.
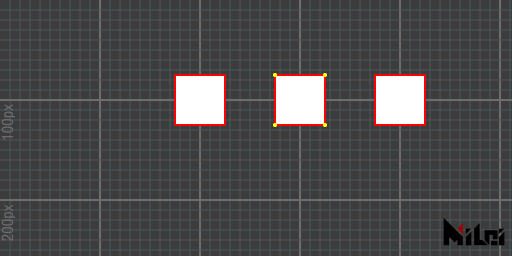
dot.lua
version3()
fill(1)
move(200, 100, 0)
stroke(1, 0, 0)
rect(50)
move(100, 0, 0)
dot(1, 1, 0)
rect(50)
move(100, 0, 0)
noDot()
rect(50)
wireframe
wireframe() enables wireframe mode.
noWireframe
noWireframe() disables wireframe mode.
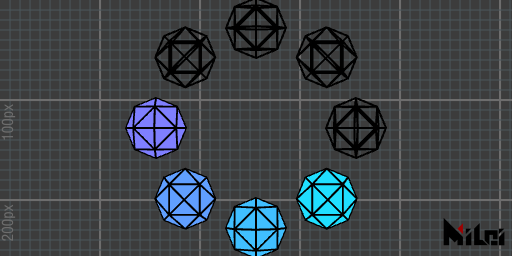
wireframe.lua
version3()
n = 8
dim3()
move(width/2, height/2)
for i = 1, n do
if i > n // 2 then wireframe()
else noWireframe() end
beginGroup()
rotateZ(d2r(i * 360 / n))
move(100, 0, 0)
fill(i/n, 1-i/n, 1)
ball(30, 1)
endGroup()
end
blendAlpha
blendAlpha() enables blending mode.
noBlendAlpha
noBlendAlpha() disables blending mode.
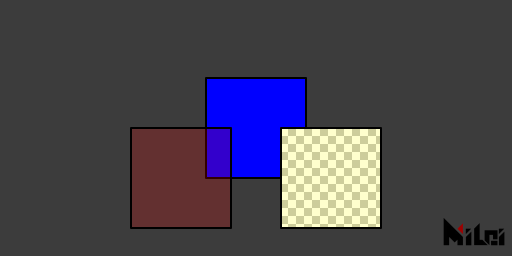
blendAlpha.lua
version3()
castTex(OUTPUT, INPUT)
move(200, 100, 0)
fill(1, 0, 0, 0.2)
rect(80)
move(100, 0, 0)
noBlendAlpha()
fill(1, 0, 0, 0.2)
rect(80)
back
When filled with a transparent color, back() displays the backside of the object. Disabled by default.
noBack
noBack() disables backface rendering mode.
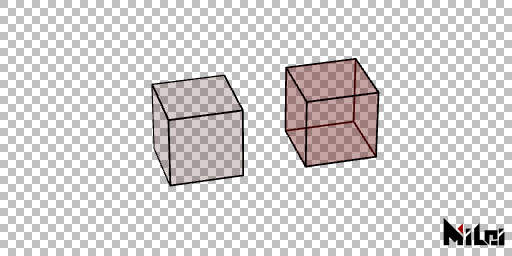
back.lua
version3()
dim3()
fill(1, 0, 0, 0.2)
rotateX(d2r(30))
rotateY(d2r(-15))
move(200, 180, 0)
cube(80)
move(150, 0, 0)
back()
cube(80)
pure
pure() uses pure color mode to render the scene. Enabled by default.
anime, phong, and pure are three materials that cannot be applied simultaneously. Enabling one will disable the others.
phong
phong(ambient, diffuse, specular, specularPower)switches to phong mode and sets the ambient reflection intensity to ambient, diffuse reflection intensity to diffuse, and specular intensity to specular. specularPower determines the specular attenuation level; the larger it is, the faster the specular attenuates.phong()switches to phong material mode without changing settings.
- The default scene has no light sources, so you need to use functions like getLight(), ambientLight(), parallelLight(), or pointLight to get light sources.
- If the rendered object is still pure black under the premise of having light sources, check if normals are correct by calling normal.
- Each parameter's initial value: ambient: 1, diffuse: 1, specular: 1, specularPower: 1.
- anime, phong, and pure are three materials that cannot be applied simultaneously. Enabling one will disable the others.
- Execute dim3() before using.
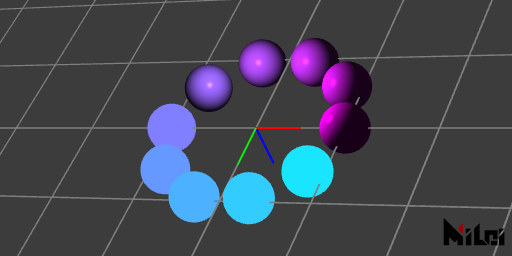
phong.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
grid()
coord()
n = 10
beginGroup()
move(0, 0, -100)
pointLight()
endGroup()
for i = 1, n do
beginGroup()
rotateZ(d2r(i * 360 / n))
move(100, 0, 0)
fill(i/n, 1-i/n, 1)
if(i <= n // 2) then pure()
else phong() end
ball(25)
endGroup()
end
anime
anime(ambient, diffuse, specular, specularPower, diffuseThreshold, specularThreshold).anime()switches to anime material mode without changing settings.
- Anime material is developed based on phong. Therefore, the first four parameters — ambient, diffuse, specular, and specularPower — are the same as in phong. The remaining two parameters, diffuseThreshold and specularThreshold, set the thresholds for diffuse and specular reflection. When diffuse reflection brightness exceeds the threshold, it is set as a highlight; if it is below, it is set as a shadow. Similarly, specularThreshold sets the threshold for highlights.
- Anime material has anti-aliasing optimization; if you have anti-aliasing enabled (enabled by default), the light and shadow transition edges will be anti-aliased. Disabling anti-aliasing settings in the plugin panel can turn off edge anti-aliasing.
- Initial value for each parameter: ambient:1, diffuse:1, specular:1, specularPower:1, diffuseThreshold:0.5, specularThreshold:0.8.
- Anime, phong, and pure are three materials that cannot be applied simultaneously. Enabling one will disable the others.
- Execute dim3() before using.
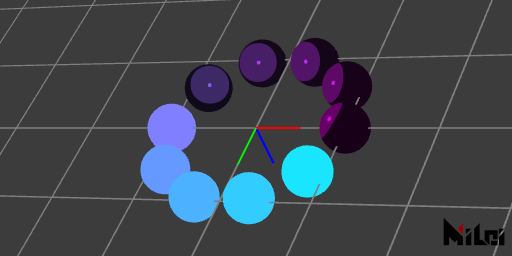
anime.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
grid()
coord()
n = 10
beginGroup()
move(0, 0, -100)
pointLight()
endGroup()
for i = 1, n do
beginGroup()
rotateZ(d2r(i * 360 / n))
move(100, 0, 0)
fill(i/n, 1-i/n, 1)
if(i <= n // 2) then pure()
else anime() end
ball(25)
endGroup()
end
rgba
rgba() is the mode for direct RGBA output, enabled by default.
- rgba, depth, and normal are three modes that cannot be active simultaneously; turning on one will turn off the other two.
- Materials can be used in this mode.

rgba.lua
version3()
dim3()
background(1)
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
n = 10
beginGroup()
move(0, 0, -100)
pointLight()
endGroup()
rgba()
-- depth()
-- normal()
noStroke()
for x = 1, n do
for y = 1, n do
for z = 1, n do
beginGroup()
fill(x/n, y/n, z/n)
move(map(x, 1, n, -n/2, n/2) * 50, map(y, 1, n, -n/2, n/2) * 50, map(z, 1, n, -n/2, n/2) * 200)
ball(10, 2)
endGroup()
end
end
end
depth
depth(blackDistance, whiteDistance) is a mode that outputs depth as brightness information. For example, to output a depth map, you can specify blackDistance and whiteDistance to set the distance from the camera at which black or white is rendered. A linear interpolation of gray will be done for distances in between. If you set blackDistance and whiteDistance to the same value, the specified value will be used as a threshold to output pure black or pure white.
- rgba, depth, and normal are three modes that cannot be active simultaneously; turning on one will turn off the others.
- This mode ignores materials.
- Execute dim3() before using.
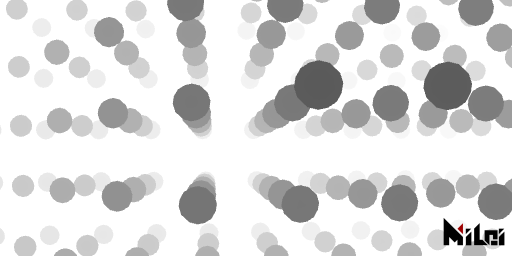
depth.lua
version3()
dim3()
background(1)
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
n = 10
beginGroup()
move(0, 0, -100)
pointLight()
endGroup()
-- rgba()
depth()
-- normal()
noStroke()
for x = 1, n do
for y = 1, n do
for z = 1, n do
beginGroup()
fill(x/n, y/n, z/n)
move(map(x, 1, n, -n/2, n/2) * 50, map(y, 1, n, -n/2, n/2) * 50, map(z, 1, n, -n/2, n/2) * 200)
ball(10, 2)
endGroup()
end
end
end
normal
normal(faceToCamera, normalize)switches to normal mode and modifies faceToCamera and normalize variables.normal(faceToCamera)switches to normal mode and only modifies the faceToCamera variable.normal()simply switches to normal mode.
faceToCamerais a boolean value that controls whether normals are generated from the camera's perspective.normalizeis a boolean value that specifies whether to output normalized normals (length 1).- Initial values: faceToCamera: true, normalize: true.
- rgba, depth, and normal are three modes that cannot be active simultaneously; turning on one will turn off the others.
- This mode ignores materials.
- Execute dim3() before using.

normal.lua
version3()
dim3()
background(0.5, 0.5, 1)
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
n = 10
beginGroup()
move(0, 0, -100)
pointLight()
endGroup()
-- rgba()
-- depth()
normal()
noStroke()
for x = 1, n do
for y = 1, n do
for z = 1, n do
beginGroup()
fill(x/n, y/n, z/n)
move(map(x, 1, n, -n/2, n/2) * 50, map(y, 1, n, -n/2, n/2) * 50, map(z, 1, n, -n/2, n/2) * 200)
ball(10, 2)
endGroup()
end
end
end
setDepth
setDepth(id, blackDistance, whiteDistance) reads the red channel of the material on the given id and sets areas with a channel value of 0 to blackDistance and areas with a value of 1 to whiteDistance, then applies the material to the depth test material.
- You can import depth sequences rendered from 3D software through this function, allowing PixelsWorld to interact with other layers at different depths.
- Execute dim3() before using.
- Valid ids:
INPUT,PARAM0~PARAM9.
newLight
A function introduced in
3.7.0.
newLight is responsible for creating a light instance. There are currently three built-in light instances: ambient light, point light, and parallel light.
- Create an ambient light:
newLight(AMBIENT_LIGHT, r, g, b, intensity) - Create a point light:
newLight(POINT_LIGHT, r, g, b, intensity, x, y, z, radius, smoothWidth) - Create a parallel light:
newLight(PARALLEL_LIGHT, r, g, b, intensity, tx, ty, tz)
AMBIENT_LIGHT,POINT_LIGHT,PARALLEL_LIGHTare constants.r, g, bspecify the light color, range0~1.intensityis the light intensity, range>=0.x, y, zare the coordinates of the point light.tx, ty, tzis the directional vector of the parallel light.radiusis the radius of influence of the point light (see the diagram below).
smoothWidthis the attenuation distance of the point light (see the diagram below).Return value: A positive integer id representing the light data.
Note: This function only creates the light. You also need to call activateLight to apply the light to the scene.

delLight
A function introduced in
3.7.0.
delLight is used to delete light instances.
delLight(id1)delLight(id1, id2)delLight(id1, id2, id3)...(Any number of ids can be input)
idis a positive integer representing light data, obtained from the return value of the newLight function.- Generally, you do not need to delete lights manually. PixelsWorld will automatically clear all lights at the end of each frame.
getLightInfo
A function introduced in
3.7.0.
Use getLightInfo(id) to retrieve information about the specified light.
- For ambient lights, use
type, r, g, b, intensity = getLightInfo(id)to capture light data.- For point lights, use
type, r, g, b, intensity, x, y, z, radius, smoothWidth = getLightInfo(id)to capture light data.- For parallel lights, use
type, r, g, b, intensity, tx, ty, tz = getLightInfo(id)to capture light data.
If you're unsure of the light type of a given id, you can manage light information as follows:
getLightInfo.lua
version3()
-- Create three test lights
local lightList = {
newLight(AMBIENT_LIGHT, 1, 0, 0, 1),
newLight(POINT_LIGHT, 1, 0, 0, 1, 100, 200, 300, 20, 30),
newLight(PARALLEL_LIGHT, 1, 0, 0, 1, 100, 200, 300),
}
for i, v in ipairs(lightList) do
-- Store all return values in an array
local returnList = {getLightInfo(v)}
-- Determine light type based on the first return value. (Note: Lua arrays start indexing from 1, not 0)
if (returnList[1] == AMBIENT_LIGHT) then
println("Ambient light! Its intensity is: " .. returnList[5])
elseif (returnList[1] == POINT_LIGHT) then
println("Point light! Its radius is: " .. returnList[9])
elseif (returnList[1] == PARALLEL_LIGHT) then
println("Parallel light! Its x component of direction is: " .. returnList[6])
end
end
-- Deleting lights is optional
delLight(table.unpack(lightList))
activateLight
A function introduced in
3.7.0.
Activates the light and makes it affect the output color of all 3D objects drawn later.
activateLight(id1)activateLight(id1, id2)activateLight(id1, id2, id3)...(Any number of ids can be input)
idis a positive integer representing light data, obtained from the return value of the newLight function.
deactivateLight
A function introduced in
3.7.0.
Deactivates the light, preventing it from affecting the output color of all 3D objects drawn later.
deactivateLight(id1)deactivateLight(id1, id2)deactivateLight(id1, id2, id3)...(Any number of ids can be input)
idis a positive integer representing light data, obtained from the return value of the newLight function.getActivatedLight
A function introduced in
3.7.0.
Retrieve the ids of all activated lights in the current environment.
getActivatedLight()
- Returns: The ids of all lights activated by activateLight (the number of return values is 0 or more).
- If you prefer all return values to be packaged in a list, use
idList = {getActivatedLight()}.
setActivatedLight
A function introduced in
3.7.0.
Clear all activated lights in the environment and reset activated lights.
setActivatedLight()clears all lights in the environment.setActivatedLight(id1)clears all lights in the environment and activates the light indicated by id1.setActivatedLight(id1, id2)clears all lights in the environment and activates the lights indicated by id1 and id2....(Any number of ids can be input)
- To simply append lights without clearing existing ones, use activateLight.
fetchLight
A function introduced in
3.7.0.
Fetch light information from an Ae scene with the specified name, create light source instances internally in PixelsWorld based on the fetched parameters, and return the ids of these light instances.
fetchLight(matchName)fetchLight()is equivalent tofetchLight("*")
- matchName rules: If the string does not end with
"*", it will search for lights named matchName in the layers of the current Ae composition and add them to the scene; if it ends with"*", all lights starting with matchName will be added to the scene.Currently supported Ae light types: ambient, point, parallel.
Returns: One or more ids of light data that match
matchName(the number of return values is 0 or more).Note: This function only creates light instances. To have the light instances affect the scene, you need to call activateLight in combination.
ambientLight
Since version
v3.7.0, this function is not recommended. Please use newLight instead.
ambientLight(r, g, b, intensity)ambientLight()is equivalent toambientLight(1, 1, 1, 1)ambientLight(brightness)is equivalent toambientLight(brightness, brightness, brightness, 1)ambientLight(brightness, intensity)is equivalent toambientLight(brightness, brightness, brightness, intensity)ambientLight(r, g, b)is equivalent toambientLight(r, g, b, 1)
- Creates an ambient light effective for all objects in the scene.
- This light ignores the direction of object normals; it can illuminate objects even if the normals are facing the opposite direction.
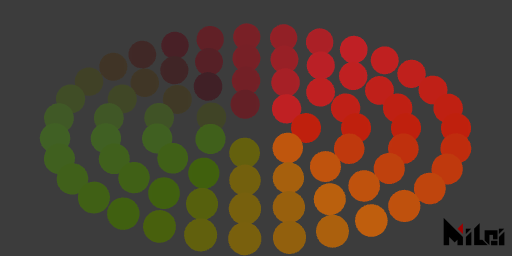
al.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
n = 4
phong()
ambientLight(1, 0.5, 0.2, 10)
noStroke()
for r = 1, n do
local ra = r * 50
local cn = math.floor(ra * TPI / 40)
for i = 1, cn do
beginGroup()
rotateZ(d2r(i/cn*360))
fill(hsl2rgb(i/cn, 0.5, 0.5))
move(ra, 0, 0)
ball(15, 3)
endGroup()
end
end
pointLight
Since version
v3.7.0, this function is not recommended. Please use newLight instead.

pointLight(r, g, b, intensity, radius, smoothWidth)pointLight()is equivalent topointLight(1, 1, 1, 1, 1000, 1000)pointLight(brightness, intensity)is equivalent topointLight(brightness, brightness, brightness, intensity, 1000, 1000)pointLight(r, g, b)is equivalent topointLight(r, g, b, 1, 1000, 1000)pointLight(r, g, b, intensity)is equivalent topointLight(r, g, b, intensity, 1000, 1000)pointLight(r, g, b, intensity, radiusAndSmoothWidth)is equivalent topointLight(r, g, b, intensity, radiusAndSmoothWidth, radiusAndSmoothWidth)
- Creates a point light source at the current drawing Paintbrush coordinate origin.
- This light is affected by the direction of object normals; objects with normals facing away will not produce diffuse reflection and highlights but can still receive ambient light from point sources.
radiusdenotes the illumination radius; light intensity decreases fromradiustoradius+smoothWidth.
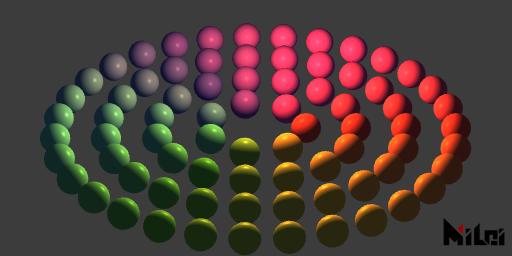
pl.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
n = 4
phong()
ambientLight(0.2, 0.5, 1, 2)
beginGroup()
move(0, 0, -100)
pointLight(1, 0.5, 0.2, 2, 500, 100)
endGroup()
noStroke()
for r = 1, n do
local ra = r * 50
local cn = math.floor(ra * TPI / 40)
for i = 1, cn do
beginGroup()
rotateZ(d2r(i/cn*360))
fill(hsl2rgb(i/cn, 0.5, 0.5))
move(ra, 0, 0)
ball(15, 3)
endGroup()
end
end
parallelLight
Since version
v3.7.0, this function is not recommended. Please use newLight instead.
parallelLight(r, g, b, intensity, tx, ty, tz)
- Generates a parallel light globally with a direction of
(tx, ty, tz).
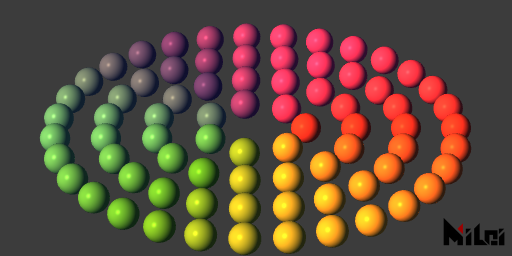
pll.lua
version3()
dim3()
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
n = 4
phong()
ambientLight(0.2, 0.5, 1, 2)
parallelLight(1, 0.5, 0.2, 2, 1, -1, 1)
noStroke()
for r = 1, n do
local ra = r * 50
local cn = math.floor(ra * TPI / 40)
for i = 1, cn do
beginGroup()
rotateZ(d2r(i/cn*360))
fill(hsl2rgb(i/cn, 0.5, 0.5))
move(ra, 0, 0)
ball(15, 3)
endGroup()
end
end
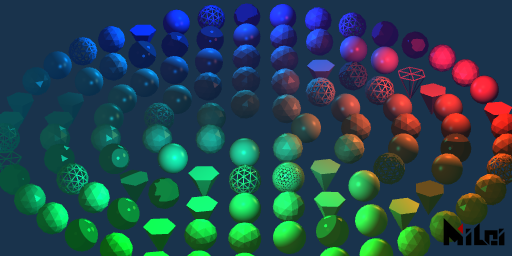
light_effects.lua
version3()
dim3()
background(0.1, 0.2, 0.3)
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
math.randomseed(1)
n = 5
ambientLight(0.2, 0.5, 1, 1)
parallelLight(1, 0.5, 0.2, 0.1, 1, -1, 1)
beginGroup()
move(200, 0, -100)
pointLight(1, 0.5, 0.2, 1, 200, 100)
endGroup()
beginGroup()
move(-30, 200, -100)
pointLight(0, 1, 1, 1, 200, 100)
endGroup()
beginGroup()
move(-30, -200, -100)
pointLight(0, 1, 1, 1, 200, 100)
endGroup()
noStroke()
for r = 1, n do
local ra = r * 50
local cn = math.floor(ra * TPI / 40)
for i = 1, cn do
beginGroup()
rotateZ(d2r(i/cn*360))
fill(hsl2rgb(i/cn, r/n, 0.6))
move(ra, 0, 0)
if math.random() < .15 then
wireframe()
else noWireframe() end
if math.random() < .15 then
anime()
else phong() end
if math.random() < .8 then
if math.random() < .3 then
ball(15, 3)
else ball(15, 2) end
else cone(15, 30, 6) end
endGroup()
end
end
clearLight
Since version
v3.7.0, this function is not recommended. Consider using deactivateLight, delLight, or setActivatedLight instead.
clearLight() clears all lights in the scene.
getLight
Since version
v3.7.0, this function is not recommended. Use a combination of fetchLight and activateLight instead.
getLight(matchName)getLight()is equivalent togetLight("*")
- Retrieves lights in the current composition that match the matchName.
- matchName rules: If the string does not end with
"*", it searches for lights named matchName in the layers of the current Ae composition and adds them to the scene. If it ends with"*", all lights starting with matchName are added to the scene.- Currently supported Ae light types: ambient, point, parallel.
aeCamera
aeCamera() uses the current scene camera from Ae as the camera for the PixelsWorld scene.
lookAt
lookAt(eyePosX, eyePosY, eyePosZ, objPosX, objPosY, objPosZ, upVecX, upVecY, upVecZ)sets the camera position and orientation.lookAt(eyePosX, eyePosY, eyePosZ, objPosX, objPosY, objPosZ)is equivalent tolookAt(eyePosX, eyePosY, eyePosZ, objPosX, objPosY, objPosZ, 0, -1, 0)
eyePosis your eye's position,objPosis the position of the object you want to look at, andupVecis the direction pointing from the top of your head.- Note that the Y-axis in Ae default points downward, so you generally need
upVecto be (0, -1, 0).eyePosandobjPosshould not be too close (recommended distance is no less than1e-7).upVecshould not be parallel to your line of sight.upVeclength should not be too small.
viewSpace
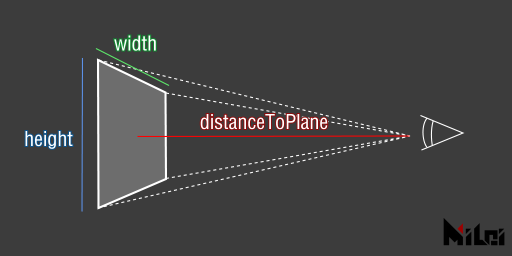
viewSpace(width, height, distanceToPlane, farLevel)viewSpace(width, height, distanceToPlane)is equivalent toviewSpace(width, height, distanceToPlane, 4)
widthandheightare the dimensions of the camera's far plane.- The perpendicular distance from the camera to the camera's far plane is
distanceToPlane.farLevel * distanceToPlaneis the distance to the farthest plane; objects beyond this distance will not be rendered. Typically, settingfarLevelto 4 is sufficient. If your scene is very large, this value can be set higher, which only affects whether distant objects are rendered. Setting this value too high might affect the depth testing precision of nearby objects.
strokeWidth
strokeWidth(width) sets the thickness of the stroke.
Default value: 2

strokeWidth.lua
version3()
background(1)
move(100, 100)
for i = 1, 30 do
move(10, 0)
strokeWidth(i/8)
line(0, 0, 0, 100)
end
strokeDivision
strokeDivision(level) sets the subdivision level of the stroke.
Default value: 3
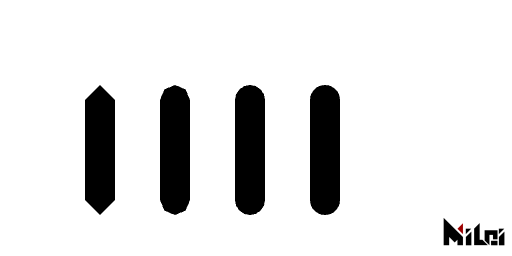
strokeDivision.lua
version3()
background(1)
strokeWidth(30)
move(100, 100)
for i = 0, 3 do
strokeDivision(i)
line(0, 0, 0, 100)
move(75, 0)
end
strokeGlobal
strokeGlobal() draws lines in global mode, with line thickness unaffected by scale.
- Default is local mode
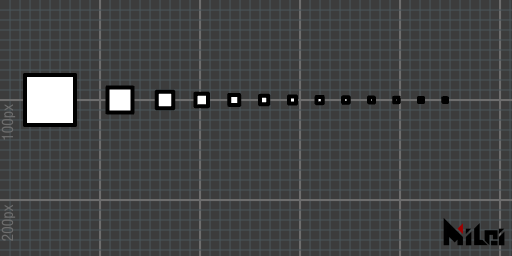
strokeGlobal.lua
version3()
strokeWidth(4)
strokeGlobal()
move(50, 100)
beginGroup()
for i = 1, 13 do
beginGroup()
scale(1/i)
rect(50)
endGroup()
move(50/i + 20, 0)
end
endGroup()
strokeLocal
strokeLocal() draws lines in local mode, with line thickness affected by scale.
- Default is local mode

strokeLocal.lua
version3()
strokeWidth(4)
strokeLocal()
move(50, 100)
beginGroup()
for i = 1, 13 do
beginGroup()
scale(1/i)
rect(50)
endGroup()
move(50/i + 20, 0)
end
endGroup()
dotRadius
dotRadius(radius) sets the thickness of the dot.
- Default value: 2
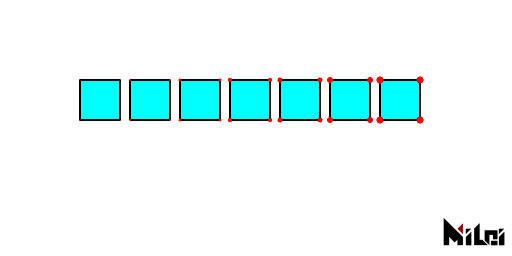
dotRadius.lua
version3()
background(1)
fill(0, 1, 1)
dot(1, 0, 0)
move(100, 100)
for i = 1, 7 do
dotRadius(i/2)
rect(40)
move(50, 0)
end
dotDivision
dotDivision(level) sets the subdivision level of the dot (non-negative integer, maximum 7).
- Default value: 3
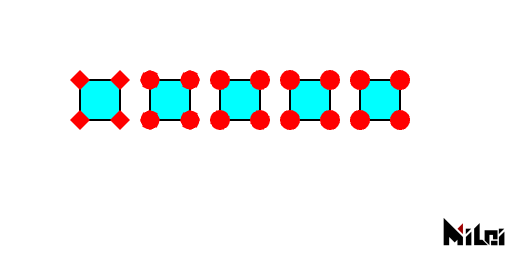
dotDivision.lua
version3()
background(1)
fill(0, 1, 1)
dot(1, 0, 0)
dotRadius(10)
move(100, 100)
for i = 0, 4 do
dotDivision(i)
rect(40)
move(70, 0)
end
dotGlobal
dotGlobal() draws dots in global mode, with dot radius unaffected by scale.
- Default is local mode
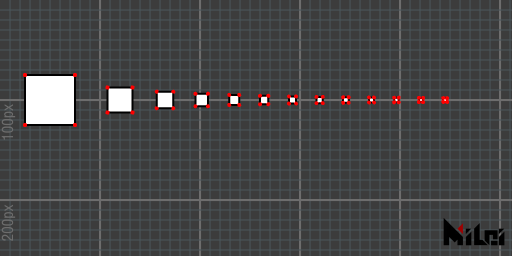
dotGlobal.lua
version3()
dot(1, 0, 0)
dotGlobal()
move(50, 100)
beginGroup()
for i = 1, 13 do
beginGroup()
scale(1/i)
rect(50)
endGroup()
move(50/i + 20, 0)
end
endGroup()
dotLocal
dotLocal() draws dots in local mode, with dot radius affected by scale.
- Default is local mode
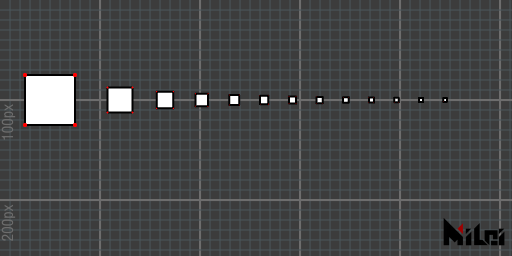
dotLocal.lua
version3()
dot(1, 0, 0)
dotLocal()
move(50, 100)
beginGroup()
for i = 1, 13 do
beginGroup()
scale(1/i)
rect(50)
endGroup()
move(50/i + 20, 0)
end
endGroup()
smooth
smooth() draws with anti-aliasing mode.
Default is on. The anti-aliasing strength can be adjusted in the plugin panel.
noSmooth
noSmooth() draws without anti-aliasing mode.
This function takes precedence over anti-aliasing settings in the plugin panel.
r2d
r2d(radians) converts radians to degrees, returning the degree value.
d2r
d2r(degrees) converts degrees to radians, returning the radian value.
map
map(value, in1, in2, out1, out2) maps the value value from the range in1~in2 to out1~out2.
When
in1equalsin2, the function returnsout1ifvalue < in1, otherwise it returnsout2.
clamp
clamp(value, lower, upper) clamps the value value within the range [lower, upper], returning the clamped value.
- New function in
v3.2.0.- That is, when
valueis betweenlowerandupper, it returnsvalue; ifvalueis less thanlower, it returnslower; ifvalueis greater thanupper, it returnsupper.
step
step(value, threshold) returns 0 when value < threshold, otherwise returns 1.
- New function in
v3.2.0.smoothStep
smoothStep(value, lower, upper) returns 0 when value < lower, 1 when value > upper, and performs smooth interpolation between lower and upper based on value.
Interpolation formula:
- New function in
v3.2.0.
bezier
bezier(t, p0, p1, ..., pn) performs n-th order Bezier interpolation on p0, p1, ..., pn, returning the interpolated result.
Interpolation formula:
- New function in
v3.2.0.- The maximum value of
nis66.
Color Conversion
xxx2xxx allows conversions as shown in the diagram below:
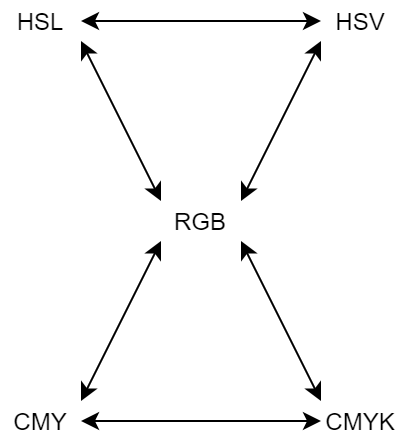
For example, if you want to convert color data from hsl format to rgb, use the function: hsl2rgb, with three input values and three return values.
All color data is converted within the range 0~1.
- New function in
v3.2.0.
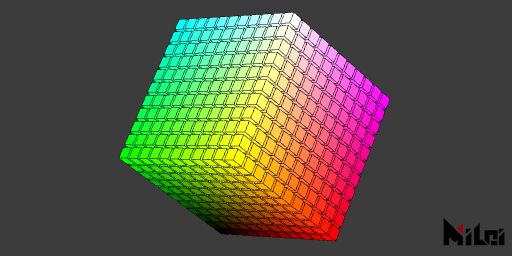
color_convert.lua
version3()
dim3()
strokeWidth(0.5)
stroke(0)
move(width/2, height/2, 0)
for x = -5, 5 do
for y = -5, 5 do
for z = -5, 5 do
beginGroup()
move(x*15, y*15, z*15)
fill(cmy2rgb(x/10 + 0.5, y/10 + 0.5, z/10 + 0.5))
cube(12)
endGroup()
end
end
end
utf8ToLocal
utf8ToLocal(str) converts a unicode string to a local string, returning the locally encoded string.
If you're using Lua's
iomodule and encounter a path with utf8 characters that cannot be read, use this function to convert the path encoding.
localToUtf8
localToUtf8(str) converts a local string to a unicode string, returning the unicode encoded string.
getGLInfo
getGLInfo() retrieves information about the current graphics card. Returns a string.
getDrawRecord
getDrawRecord(needStringFormat)outputs the drawing record information of the current scene.needStringFormatis a Boolean value; if true, it outputs a string, if false, it outputs a Lua table.getDrawRecord()is equivalent togetDrawRecord(true).
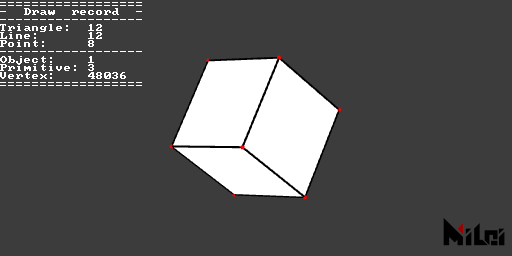
printDrawRecord.lua
version3()
dot(1, 0, 0)
move(width/2, height/2)
dim3()
cube()
println(getDrawRecord())
getStatus
getStatus(needStringFormat)can output the current draw status information.needStringFormatis a Boolean value; if true, it outputs a string, if false, it outputs a Lua table.getStatus()is equivalent togetStatus(true).
getStatus.lua
version3()
move(width/2, height/2)
dim3()
cube()
println(getStatus())
getAudio
Ensure you have
v3.4.0+version of PixelsWorld.
getAudio([startTime, duration[, id[, sampleRate, startFrequency, endFrequency[, resolution]]]])retrieves audio information, returning six tables: two waveform sampling tables (left and right channels), two FFT result tables (left and right channels), and two spectrum tables (left and right channels).- Omitted fields will be filled with audio setting data from the plugin panel.
- Left channel waveform (-1~1)
- Right channel waveform (-1~1)
- Left channel FFT (0~positive infinity)
- Right channel FFT (0~positive infinity)
- Left channel spectrum (0~positive infinity)
- Right channel spectrum (0~positive infinity)
waveInfo.lua
version3()
castTex(OUTPUT,INPUT)
local wl, wr, ftl, ftr, specl, specr = getAudio()
local nm = math.floor(height/8);
for i = 1, nm do
local wid = math.max(math.floor(i/nm * #wl), 1)
local fid = math.max(math.floor(i/nm * #specl), 1)
print(string.format("%8.5f", wl[wid]), wl[wid] * 4, 0, -wl[wid] * 4)
print(" < L R > ", 1, 0, 0, 0)
print(string.format("%8.5f", wr[wid]), wr[wid] * 4, 0, -wr[wid] * 4)
print(" < Wave FFT > ", 0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
print(string.format("%8.5f", specl[fid]), specl[fid], 0, 0)
print(" < L R > ", 1, 0, 0, 0)
print(string.format("%8.5f", specr[fid]), 0, 0, specr[fid])
println("")
end
saveString
saveString(utf8_path, string) saves a string as a text format in the local system.
loadString
loadString(utf8_path) reads a local text file, returning the string.
getColor
getColor(id, x, y) returns the pixel value at coordinate (x, y) of the texture id, with r, g, b, a as four double-precision floating-point numbers.
getColor(x, y) is equivalent to getColor(INPUT, x, y).
- When
getColoris used before drawing any scene (i.e., immediately afterversion3()), the function is most efficient. UsinggetColorduring scene drawing is very inefficient as Lua operates on the CPU, and all textures are sent to your graphics card during drawing, making communication between the GPU and CPU costly.- Valid ids are
INPUT,OUTPUT,PARAM0~PARAM9.
setColor
setColor(x, y, r, g, b, a) sets the pixel value at coordinate (x, y) of the OUTPUT texture.
- Efficiency is highest when using
setColorbefore drawing any scene (i.e., immediately afterversion3()).
getSize
getSize(id) returns the size of the texture id (two doubles, width, and height).
When you change scene downsample (e.g., half, quarter), the returned size may jitter by 0~4 pixels due to Ae’s downsampling feature. However, this jitter does not change over time. When downsampling is turned off, this function guarantees the correct layer size.
shadertoy
shadertoy(code) executes code from Shadertoy.
- Not all Shadertoy code is supported.
glsl
glsl(code) executes Fragment stage code.
cmd
cmd(code) executes a cmd command.
If the command runs successfully, the first return value is true; otherwise, it is nil. After the first return value, the function returns a string and a number. As follows:
- "exit": The command ended normally; the following number is the command’s exit status code.
- "signal": The command was interrupted by a signal; the next number is the signal that interrupted the command.
lua
lua(code) executes Lua code.
runFile
runFile(utf8_path) reads a local file as a txt file and executes it as Lua code.
Supports utf8 by default, so no need to call
utf8ToLocalfor conversion.
txt
txt(utf8_path) reads a local file as a txt file and returns a string.
Supports utf8 by default, so no need to call
utf8ToLocalfor conversion.