Filter System
Please ensure you have PixelsWorld
v3.6.0+
The filter system is an encapsulation of rectangle shaders, allowing you to quickly develop post-processing shaders for overall image effects.
Through this chapter, you can quickly understand and learn how to use the filter system of PixelsWorld.
- newFilter Create Filter
- runFilter Run Filter
- delFilter Delete Filter
- setFilterUniform Set Filter Uniforms
- setFilterDrawto Set Output Image
- newFilterModule Create Filter Module
- Advanced Application
Create Filter
Use newFilter(glslCode) to create a filter program.
- Return: A random integer representing the filter program (Filter ID)
glslCode will be inserted into the following context:
glslcode_context.glsl
#version 330 core
in vec2 uv;
out vec4 outColor;
// Your glslCode here!
Example
Note: In Lua, we use double square brackets
[[...]]to denote multiline strings
newFilter.lua
version3()
filterID = newFilter([[
void main(){
outColor = vec4(uv,0,1);
}
]])
Run Filter
Use runFilter(filterID) to run a filter program.
Example
runFilter.lua
version3()
filterID = newFilter([[
void main(){
outColor = vec4(uv,0,1);
}
]])
runFilter(filterID)
Delete Filter
Use delFilter(filterID) to delete a filter.
Usually, you don't need to delete filters, as PixelsWorld automatically deletes all filters at the end of each frame. However, it's still a good practice to delete a filter when it's no longer needed.
Example
delFilter.lua
version3()
filterID = newFilter([[
void main(){
outColor = vec4(uv,0,1);
}
]])
delFilter(filterID)
Set Filter Uniforms
Use setFilterUniform(filterID, uniformType, uniformName, data0, data1, data2, ...) to set the uniform properties you defined in a filter.
filterID: Filter ID, integer.uniformType: String representing the variable type. Supports one-dimensional data ("int","float","bool"), vectors ("vec2","vec3","vec4","ivec2"...), matrices ("mat2, mat4x3, ..."), textures ("sampler2D")uniformName: Variable name string.data0,data1,...: Floating point data. (See example for details)
Example
setFilterUniform.lua
version3()
filterID = newFilter([[
uniform float myfloat;
uniform vec2 myvec;
uniform mat3x2 mymat;
uniform sampler2D mytex1;
void main(){
outColor = vec4(myfloat,myvec[0],mymat[0][1],1) + texture(mytex1,uv);
}
]])
setFilterUniform(filterID, "float", "myfloat", math.sin(time)*0.5 + 0.5)
setFilterUniform(filterID, "vec2", "myvec", 1,2)
-- Column major, namely mymat[0][0]==1, mymat[0][1]==slider(0), mymat[0][2]==2, mymat[1][0]==3, ...
setFilterUniform(filterID, "mat3x2", "mymat", 1, slider(0), 2, 3, 4, 5)
-- Use INPUT texture as mytex1
setFilterUniform(filterID, "sampler2D", "mytex1", INPUT)
-- ** You can also set the texture you created as mytex1 **
-- myInputTexID = newTex(512,256)
-- setFilterUniform(filterID, "sampler2D", "mytex1", myInputTexID)
runFilter(filterID)
Set Output Image
Use setFilterDrawto(filterID, texID) to specify which texture the result of the filter should be placed on. For texID, refer to the Texture System.
The default output texture is
OUTPUT.
You can even perform iterative shading on an image.
See Advanced Application for details.
Create Filter Module
Use newFilterModule(glslCode) to create a filter module.
- Return: A table containing the filter ID and some utility functions.
The purpose of a filter module is to simplify your code.
If you do not use a filter module, normally you need to write a filter like this:
no_module.lua
version3()
filterID = newFilter([[
uniform float myfloat;
void main(){
outColor = vec4(myfloat,0,0,1);
}
]])
setFilterUniform(filterID, "float", "myfloat", math.sin(time)*0.5 + 0.5)
setFilterDrawto(filterID, OUTPUT)
runFilter(filterID)
delFilter(filterID)
With a filter module, you can write it like this:
no_module.lua
version3()
filter = newFilterModule([[
uniform float myfloat;
void main(){
outColor = vec4(myfloat,0,0,1);
}
]])
filter.set("float", "myfloat", math.sin(time)*0.5 + 0.5)
filter.drawto(OUTPUT)
filter.run()
filter.del()
Advanced Application
Below is a code example for channel blur:
slider 0: Blur intensitylayer 0: Blur mask
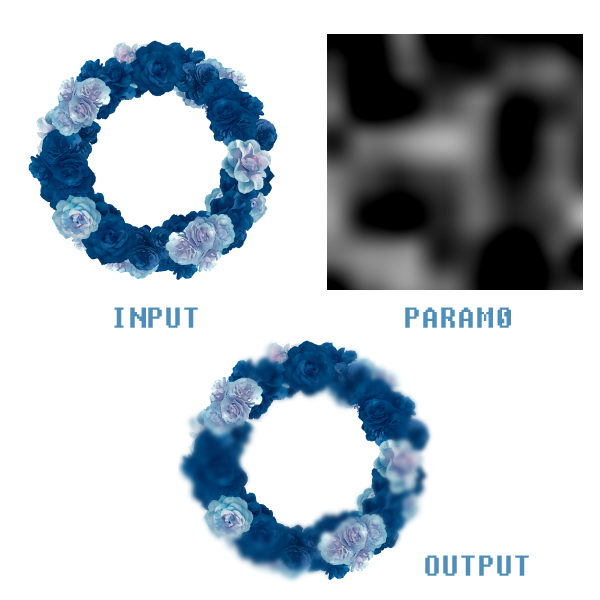
iterateFilter.lua
version3()
-- Create a temporary texture
tempTexID = newTex(width, height)
-- Copy input to temp texture
castTex(tempTexID, INPUT)
-- Blur code
blurGLSLCode = [[
uniform sampler2D in_tex;
uniform mat3 kernel;
uniform vec2 resolution;
void main()
{
vec2 xy = resolution * uv;
vec4 res = vec4(0,0,0,0);
for(int x = 0; x < 3; x++)
{
for(int y = 0; y < 3; y++)
{
vec2 curxy = xy + vec2(x-1,y-1);
res += texture(in_tex,curxy/resolution) * kernel[x][y];
}
}
outColor = res;
}
]]
-- Combine code
combineGLSLCode = [[
uniform sampler2D images[4];
uniform sampler2D masktex;
uniform mat2 uvcoord;
void main()
{
vec2 newuv = floor(uvcoord * uv * 128);
float maskv = clamp(texture(masktex, uv).r,0,1);
int maski = int(floor(maskv * images.length()));
float maskw = fract(maskv * images.length());
if(maski == images.length) maski--;
vec4 c1 = texture(images[maski], uv);
vec4 c2 = c1;
if(maski+1<images.length)
c2 = texture(images[maski+1], uv);
outColor = mix(c1, c2, maskw);
}
]]
blurFilter = newFilterModule(blurGLSLCode)
-- Set the kernel data of 3x3 Gaussian blur
-- The data can be found at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_(image_processing)
blurFilter.set("mat3", "kernel",
1.0/16, 2.0/16, 1.0/16, -- kernel[0][0], kernel[0][1], kernel[0][2]
2.0/16, 4.0/16, 2.0/16, -- kernel[1][0], kernel[1][1], kernel[1][2]
1.0/16, 2.0/16, 1.0/16) -- kernel[2][0], kernel[2][1], kernel[2][2]
blurFilter.set("vec2", "resolution", width, height)
-- Set temp texture as in_tex
blurFilter.set("sampler2D", "in_tex", tempTexID)
-- Set the temp texture as the Drawto
blurFilter.drawto(tempTexID)
middleResultTex = {}
for i=1,3 do
middleResultTex[i] = newTex(width, height)
end
-- Blur power
substep = slider(0)
-- Iterate filter 3*substep times
for i=1, 3*substep do
blurFilter.run()
if i % substep == 0 then
castTex(middleResultTex[i//substep], tempTexID)
end
end
combineFilter = newFilterModule(combineGLSLCode)
combineFilter.set("sampler2D", "images",
INPUT,
middleResultTex[1],
middleResultTex[2],
middleResultTex[3]
)
combineFilter.set("sampler2D", "masktex", PARAM0)
combineFilter.drawto(OUTPUT)
combineFilter.run()